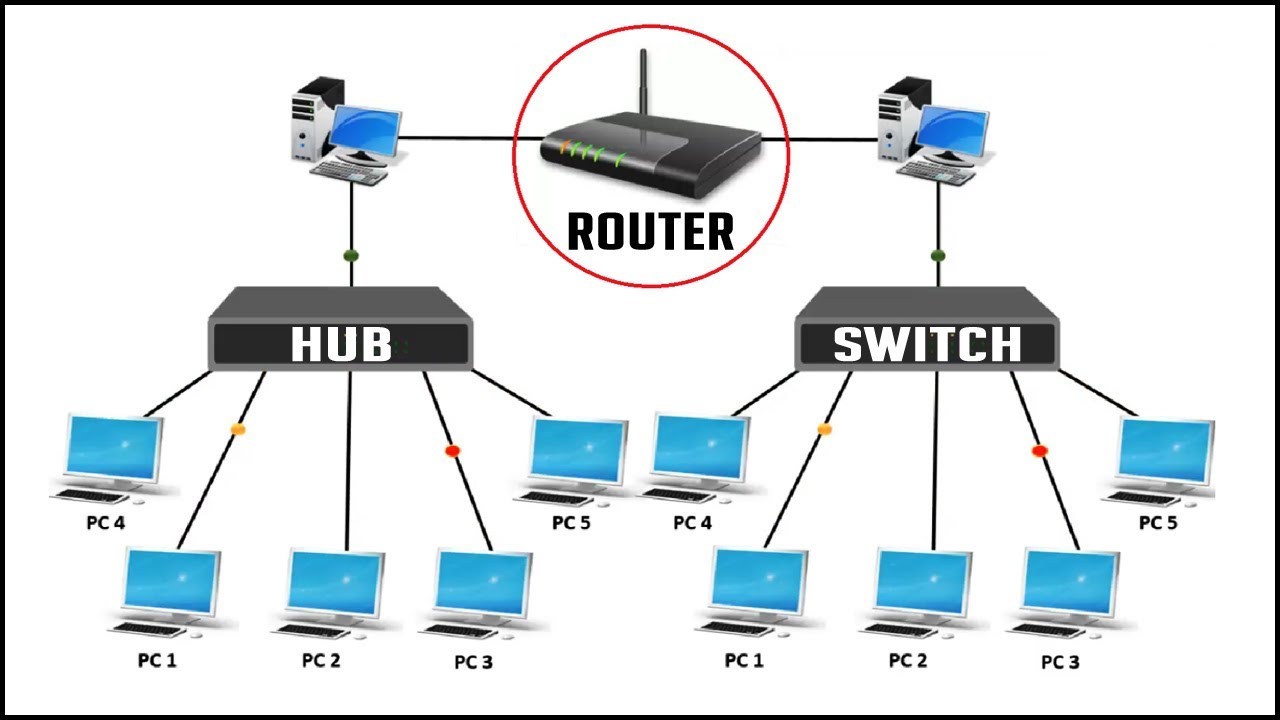
What is a Switch?
A switch is a multicast networking device that works under the Datalink layer of the OSI model and connects a bunch of computers or devices in a network. Its mainly used to send a private message and it does not waste data. A switch can easily identify which device is connected to which port by using a MAC address giving it the ability to deliver the message to a particular machine. Advantages of using a Switch Its secure since it delivers data to the specified node. It lowers the chances of frame collisions domains. It increases the bandwidth in a network. It increases the number of ports needed to connect the nodes available in a network. It operates under full-duplex. Disadvantages of using Switches
They are more expensive compared to hubs and other devices used in a network. To manage multicast packets, good planning is required. Problems can arise when transmitting traffic.
What is a hub?
A hub is a simple and inexpensive networking device that operates under the physical layer of the OSI model and connects a group of computers in a local area network (LAN). It is considered less intelligent because it does not filter the data and does not know where the data should be sent.
All information sent to a hub is automatically sent to all ports of the devices connected to it. This leads to wastage of bandwidth.
Advantages of using hubs
They have the ability to connect to the network using different physical media. They can be used to increase the network distance. Hubs are relatively cheap compared to switches and other devices in the network. Disadvantages of using a hub
It increases the chances of collision domains between packets when being transferred from one device to another. Hubs operate under half-duplex. Only one device can send or receive data at a time
Hubs share data to all the devices in a network thus making the network insecure. Hubs waste lots of bandwidth when transmitting data.
Switch vs Hub
A Hub is a broadcast device that sends data from one node to all nodes but a Switch is a multicast device that can send data to a particular node. A Hub supports half-duplex i.e., only one device can send or receive data at a time while a switch supports full-duplex i.e., both devices can send and receive data at the same time. A switch is located on the second layer of the OSI model while a Hub is located on the first layer. What is a Router? A Router is a networking device that operates under the network layer of the OSI model and is used to connect two or more networks. It is a device that establishes a common link between networks to enable data flow between them. Advantages of the router
Using dynamic routing algorithm, it can choose the best path through the internetwork. It creates collision domains to reduce network traffic. It provides connections between different network architectures. Cons of the router
They are expensive compared to hubs and switches. They have to analyze the data. This makes them slower. They have low bandwidth because of their dynamic router communication.layer in the OSI model
The Open Systems Interconnection Model(OSI Model) is a 7 layer model that is used to describe, in a pictorial way, how computer systems communicate. A switch, a router, and a hub each operate on a different layer.
A switch is located on the OSI model`s Data Link layer i.e., the second layer. The link layer is specific to the medium over which the packet is traveling. The Ethernet and Mac Address are part of this layer.
A router resides in the Network Layer of the OSI model i.e., the third layer.
A hub is located in the Physical Layer of the OSI model i.e., the first layer. Functions of each device
Change
It allows different connections of multiple devices in the same network and manages VLAN and port security settings. Learning – This is the process of acquiring the MAC addresses of paired devices. Forwarding – It is the process of forwarding network traffic from a device connected to one port of a network switch to another device connected to a different port. Layer 2 Switch Loop Prevention – In LANs, redundant connections are built to prevent the entire network from failing if one link fails. Layer 2 switch loops and broadcast storms can be caused by redundant connections. A network switch`s job is to prevent layer 2 switching loops and broadcast storms.
Router
Its major purpose is to connect many types of networks at the same time using adaptive and non-adaptive routing. The router is connected to at least two networks and decides how to deliver each data packet depending on its current knowledge of the network status. If a packet is traveling to the LAN, the router bounces it back. The packet will be toured depending on the routing table if this is not the case.
Center
A hub is a simple, inexpensive networking device that allows a group of computers to be connected to a single network.
When a hub receives a data packet (Ethernet frame) from a network device on one of its ports, it broadcasts (repeats) the packet on all its ports, i.e. on all devices. other network. A collision occurs when two network devices on the same network try to send packets at the same time. Application of each device
Change
It is commonly used in LAN to connect multiple nodes. Forward mail to a specific server – On each port, a switch, like a bridge, uses the same forwarding or filtering logic. When a host or switch on the network forwards a message to another host or switch on the same network, the switch receives the frames and decodes them to read the physical address component (MAC). of the message. Increase LAN bandwidth – The switch divides the LAN into multiple conflicting domains, each with high-speed connection, greatly improving LAN bandwidth.
router
It is commonly used in local area networks and metropolitan area networks (MAN). It handles traffic by forwarding data packets to their appropriate IP address. Traffic between these networks can be managed. It determines the best path to send packets. Center
It is similar to a switch because it is used in a local area network (LAN). It is used for network monitoring. They are also used in organizations to provide connectivity. It can be used to provision a device on the network. Data transmission method
They determine the direction in which data flows between two communicating devices. There are three kinds of transmission mode:
Simplex – In this transmission mode, data can only travel in one direction, i.e. device can only send data but not receive and receiving device can only receive but not send data. Half-Duplex – In this mode, only one device can send or receive data at a time, not both at the same time. Full-Duplex – In this mode, one device can send and receive data at the same time. Read this document for more information about the different data transfer modes.
Switches and routers support full duplex transmission. Therefore, several computers can send data at the same time.
Hub supports half-duplex transmission. So only one node can send data at a time.
Address used in each device
Switches store and use the device’s MAC address to transmit data while routers use the device’s IP address to transfer data between networks.
A hub, on the other hand, does not store any MAC/IP addresses for data transmission. data transmission
A switch transmits data from one device to another as a frame while a router transmits data from one network to another in the form of packets.
A hub transmits data from one device to another in the form of binary bits.
Inference
In this article, we looked at hubs, switches, and routers. We also looked at their features and the application of each device as used in